Two Sums: Mastering the Classic Coding Challenge
Understanding the Two Sums Problem in Depth
The Two Sums problem is a classic exercise that often pops up in coding interviews and programming challenges. It involves finding two numbers in a list that add up to a specific target sum. While it sounds simple, there are various approaches to solve it efficiently. In this article, we’ll explore the Two Sums problem, its significance in programming, and delve into different strategies for solving it.
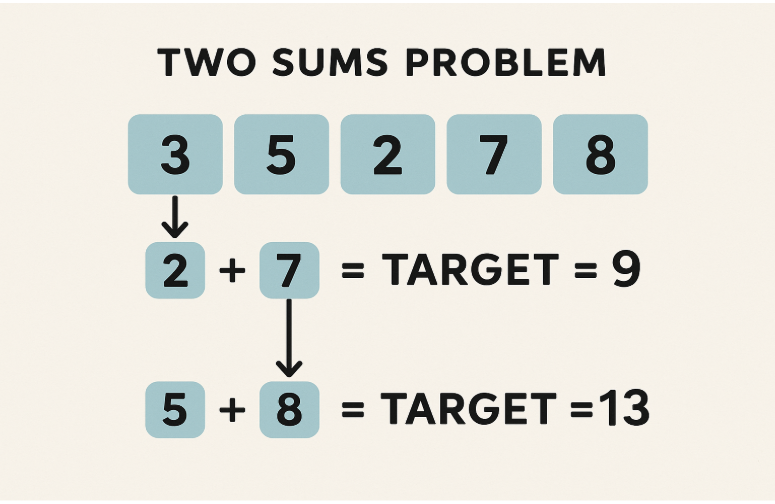
The Two Sums problem is a common algorithmic challenge. Given an array of integers and a target integer, your task is to find the indices of the two numbers that add up to the target.
Input: An array of integers nums and an integer target.
Output: Indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
For instance, consider the array nums = [2, 7, 11, 15] and target = 9. The solution would be the indices [0, 1] because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9.
Understanding the Two Sums problem begins with a grasp of its simplicity and potential complexity. While the task seems straightforward, it serves as a gateway to more intricate algorithmic challenges. The simplicity of the problem makes it an ideal candidate for introducing the fundamentals of algorithm design and computational thinking.
Moreover, the problem’s constraints, such as requiring the indices instead of the numbers themselves, add a layer of complexity. This requirement forces programmers to consider the best data structures and logic to efficiently track the indices. It is this blend of simplicity and depth that makes the Two Sums problem a staple in coding education and interviews.
Why is the Two Sums Problem Important?
1. Foundation for Algorithm Design
The Two Sums problem is a simple introduction to algorithm design and optimization. It encourages programmers to think critically about problem-solving techniques, data structures, and computational efficiency.
By tackling this problem, learners are introduced to the importance of selecting the appropriate algorithm to optimize performance. It is a practical exercise in balancing trade-offs between time complexity and space complexity, which are crucial considerations in software development. As a foundational problem, it sets the stage for more advanced algorithmic challenges, making it a vital part of a programmer’s education.
Furthermore, solving the Two Sums problem often involves analyzing different approaches and understanding their implications on performance. This cultivates a mindset of evaluating multiple solutions and choosing the most efficient one, a skill that is essential for efficient coding practices and effective software design.
2. Real-world Applications
Though it may seem abstract, the Two Sums problem has practical applications in fields like finance, data analysis, and network security. For example, it can be used to identify pairs of transactions that match a specific sum or detect anomalies in datasets.
In finance, the ability to quickly identify transactions that sum to a particular value can help in balancing accounts and detecting fraud. Similarly, in data analysis, this problem can assist in pattern recognition and the identification of trends by pinpointing specific data combinations. In network security, algorithms based on the Two Sums problem can be employed to detect unusual patterns that might indicate a breach or attack.
These applications demonstrate the problem’s versatility and relevance beyond academic exercises, showcasing its value in practical, real-world scenarios. By understanding its applications, programmers can appreciate the broader impact of their coding skills on various industries.
3. Preparation for Coding Interviews
Many tech companies, including giants like Google and Facebook, use the Two Sums problem in coding interviews. It tests a candidate’s ability to implement efficient algorithms under pressure.
The problem serves as an excellent benchmark for assessing a candidate’s problem-solving skills and their understanding of algorithm design. It requires not only technical proficiency but also the ability to articulate thought processes and justify chosen approaches. Mastery of the Two Sums problem can significantly boost a candidate’s confidence and performance in technical interviews.
Additionally, the problem’s frequent appearance in interviews underscores its importance in the software development industry. Being well-versed in solving the Two Sums problem can provide a competitive edge, preparing candidates for the challenges and expectations of technical roles in leading tech companies.
Exploring Different Solutions
There are multiple ways to solve the Two Sums problem, each with its own trade-offs in terms of time and space complexity. Let’s dive into some of the common approaches.
Brute Force Approach
The brute force method is the simplest and most intuitive approach. It involves checking each pair of numbers to see if they add up to the target.
Time Complexity: O(n²) due to the nested loops.
Space Complexity: O(1) as no additional data structures are used.
While the brute force approach is straightforward, it is not efficient for large datasets due to its quadratic time complexity. This method is useful for understanding the problem’s basic mechanics but highlights the need for more optimal solutions. It serves as a reminder of the importance of efficiency in algorithm design, especially when dealing with large inputs.
Despite its inefficiency, the brute force approach is valuable for educational purposes, providing a clear illustration of the problem’s requirements. It lays the groundwork for understanding more complex solutions by offering a baseline against which other methods can be compared.
Using a Hash Map
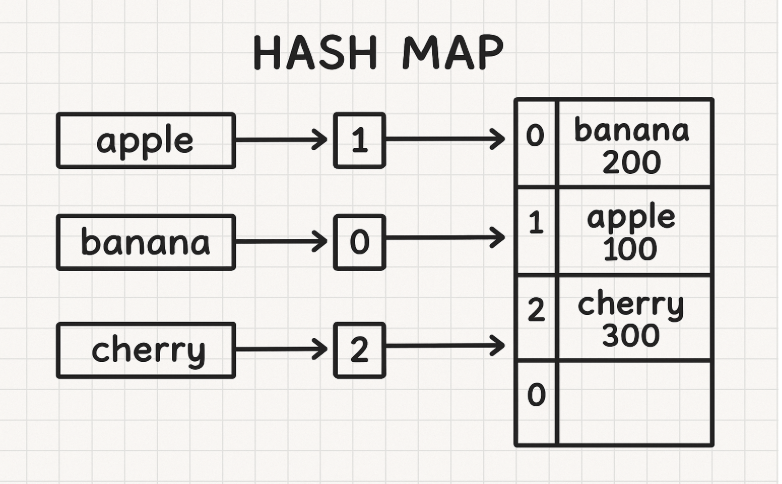
A more efficient approach utilizes a hash map to store and retrieve the needed values quickly.
Time Complexity: O(n) since we traverse the list once.
Space Complexity: O(n) for storing elements in the hash map.
The hash map approach significantly reduces the time complexity by allowing constant-time lookups. By storing each number’s complement, this method efficiently finds the solution in a single pass through the array. This demonstrates how strategic use of data structures can vastly improve algorithm performance.
Furthermore, this approach exemplifies the power of combining data structures with algorithmic logic to achieve optimal solutions. It underscores the importance of understanding various data structures and their appropriate use cases, a critical skill for any programmer.
Two-pointer Technique
The two-pointer technique is another efficient method, particularly when the list is sorted. It involves pointing to the start and end of the array, then moving pointers inward based on the sum comparison.
Time Complexity: O(n log n) due to sorting.
Space Complexity: O(1) if we disregard the space for sorting.
The two-pointer technique showcases how leveraging the properties of a sorted array can lead to efficient solutions. By systematically narrowing down the search space, it achieves a balance between simplicity and efficiency. This method is particularly useful when dealing with sorted data, highlighting the benefits of preprocessing steps like sorting.
Moreover, the two-pointer approach illustrates the creative application of algorithmic strategies to optimize problem-solving. It encourages programmers to think outside the box and consider how different techniques can be adapted to specific scenarios for better outcomes.
Fermat’s Theorem on Sums of Two Squares
Application in Number Theory
Fermat’s theorem helps in understanding the decomposition of numbers and has implications in various number theory problems. It provides a deeper insight into how numbers can be represented and manipulated.
The relationship between the Two Sums problem and Fermat’s theorem highlights the intersection between computer science and mathematics. This connection enriches the problem-solving experience by introducing mathematical elegance into algorithmic challenges. By exploring such extensions, programmers can appreciate the broader implications of their work beyond immediate applications.
Additionally, Fermat’s theorem serves as a reminder of the historical and theoretical foundations of modern algorithms. It emphasizes the role of mathematical theory in shaping the development of computational techniques, offering a fascinating perspective on the evolution of problem-solving methods.
Conclusion
The Two Sums problem is a versatile and essential challenge that serves as a stepping stone to more complex algorithmic concepts. Whether you’re preparing for a coding interview or exploring algorithm design, understanding different approaches to this problem will enhance your problem-solving skills.
By practicing the Two Sums problem, you gain valuable experience in selecting and implementing efficient algorithms, a skill that is crucial for every programmer. The problem is not just about finding two numbers; it’s about exploring the depths of algorithmic thinking and application. Embrace it as a learning opportunity and a chance to refine your coding abilities.
In essence, the Two Sums problem is a microcosm of the broader challenges faced in computer science. It embodies the core principles of algorithm design, efficiency, and real-world application. Mastering it can set the foundation for tackling more complex problems and advancing in the field of software development.